visionOS 2 HandMatcher HandVector Update to v2 and Add New FingerShape Function
HandVector
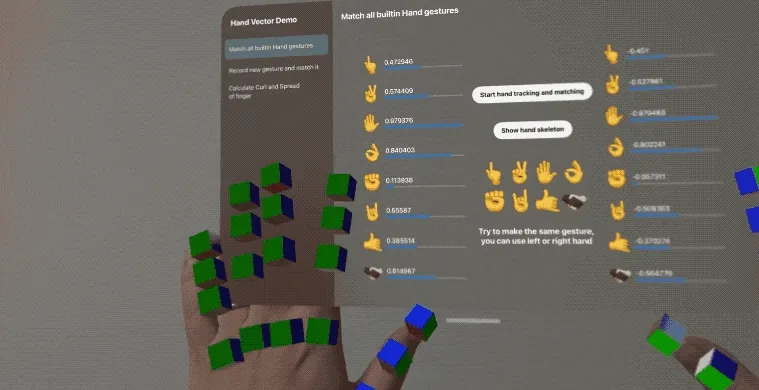
After the release of Vision Pro, the elegant gesture interaction caused a lot of heat, but unfortunately Apple did not provide a 3D gesture recognition function, not even static. So I used cosine similarity algorithm to write my own HandVector framework to achieve this function: for example, using hands to make ✌️ gestures to trigger a certain effect, and also wrote an article introducing “I open-sourced a gesture matching framework, allowing you to debug visionOS hand tracking function in emulator!”
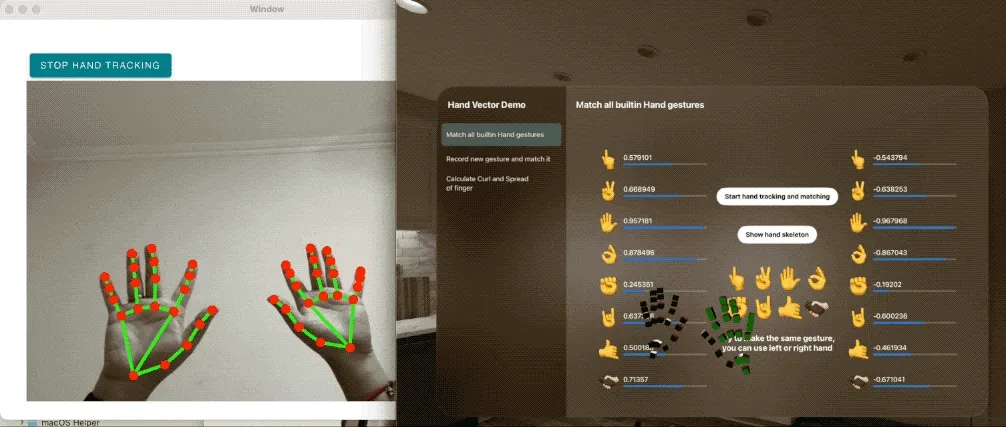
HandVector not only calculates the similarity between different static gestures, but also comes with a macOS utility class that allows you to use gesture tracking on visionOS emulator for basic gesture testing.
This HandVector 2.0 version is a big update, bringing better cosine similarity Cosine Similarity matching effect and finger shape parameter FingerShape function, more convenient for customization.
Note: HandVector 2.0 has significant API changes and is not compatible with older versions.
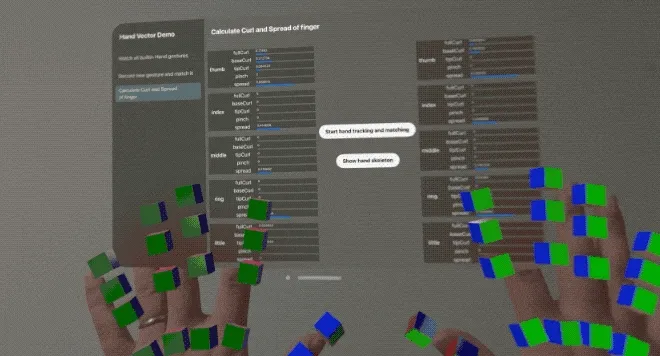
Cosine similarity calculation update
Perhaps you may wonder: how can the cosine similarity algorithm be improved? Indeed, the algorithm itself is difficult to improve, but I improved the reference coordinate system during calculation, which brought about a huge overall improvement.
Let’s first take a look at the biggest problem with the old version of the algorithm: all the vectors used in the calculation are based on the Anchor space of the hand (wrist), which will cause the direction difference of the finger joint during the gesture change process to be too large, resulting in errors in similarity calculation.
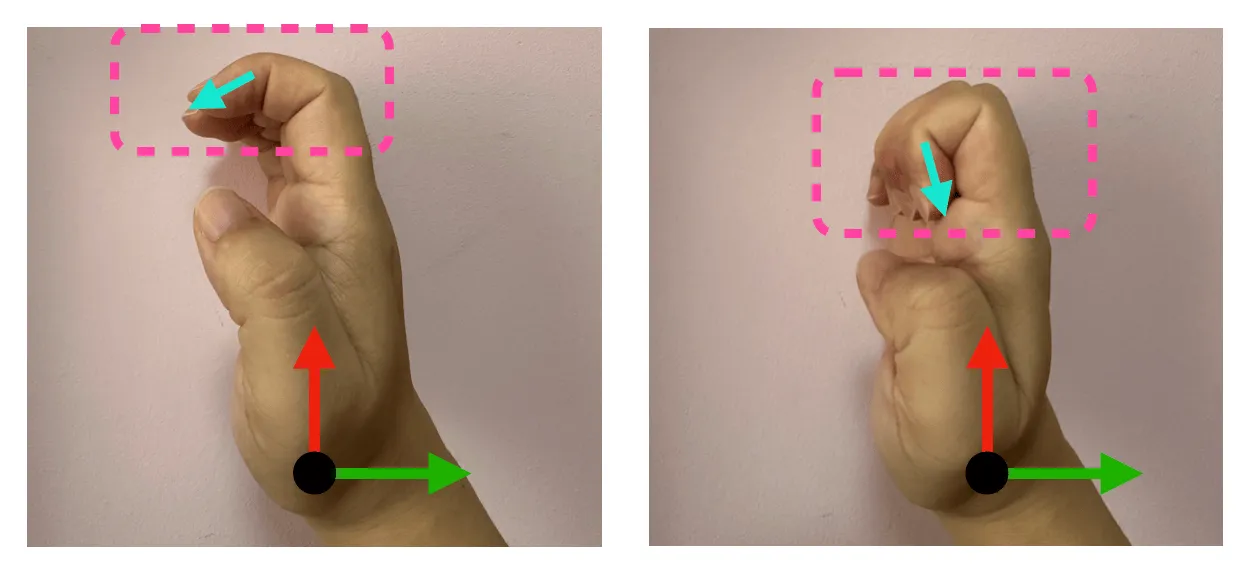
For example, in the above figure, there are two gestures, one with a half-bent finger and the other with a completely bent finger. Although they have a certain similarity, the direction of the fingertip vector is almost perpendicular to the coordinate origin, resulting in their cosine similarity being close to 0, which is obviously unreasonable.
So, in version 2.0, I improved this by using the matrix space of the parent node to calculate the vector direction, so that the similarity of the fingertip vector is greatly improved.
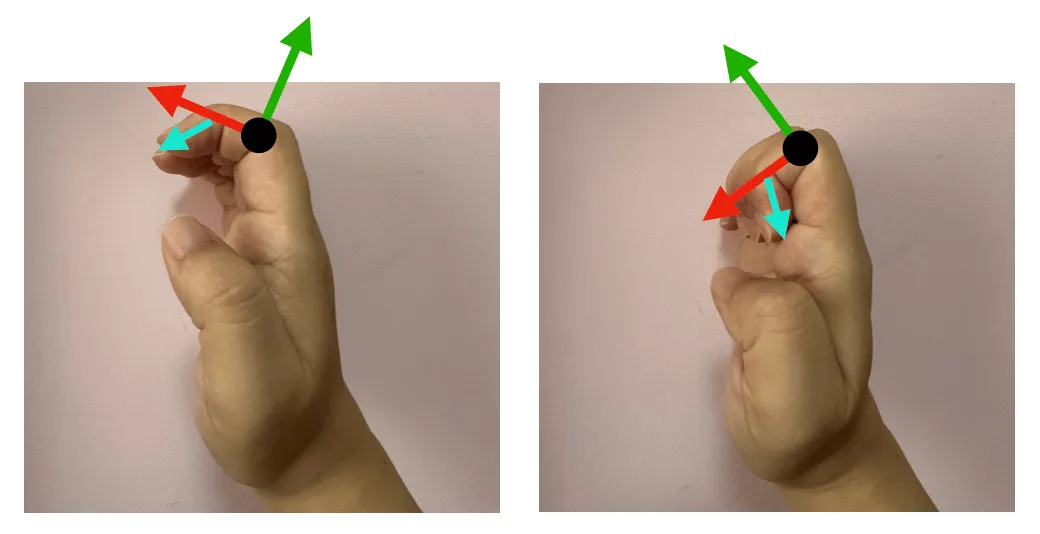
After the update, the fingertip postures of the two gestures in the above picture are highly similar. However, this brings up a new problem: coordinate conversion requires the calculation of the Inverse Matrix, will it have a performance impact? The answer is no, because ARKit provides this matrix, as shown in the figure below.

parentFromJointTransform Actually, it is the posture matrix of the current joint point relative to the parent joint, and anchorFromJointTransform is the posture matrix relative to the Anchor (wrist). We can directly save and use it without additional calculation and consumption.
Naming formula: A From B Transform = B Relative to A transform parentFromJointTransform = Joint Relative to Parent transform anchorFromJointTransform = Joint Relative to Anchor transform
Add FingerShape
The cosine similarity algorithm has high accuracy, but the parameters are difficult to understand and almost impossible to adjust. Therefore, I refer to Unity’s XRHands framework and add the FingerShape function.
It simplifies the shape of the finger into 5 parameters such as curl and separation, which are easy to understand, control, and adjust.
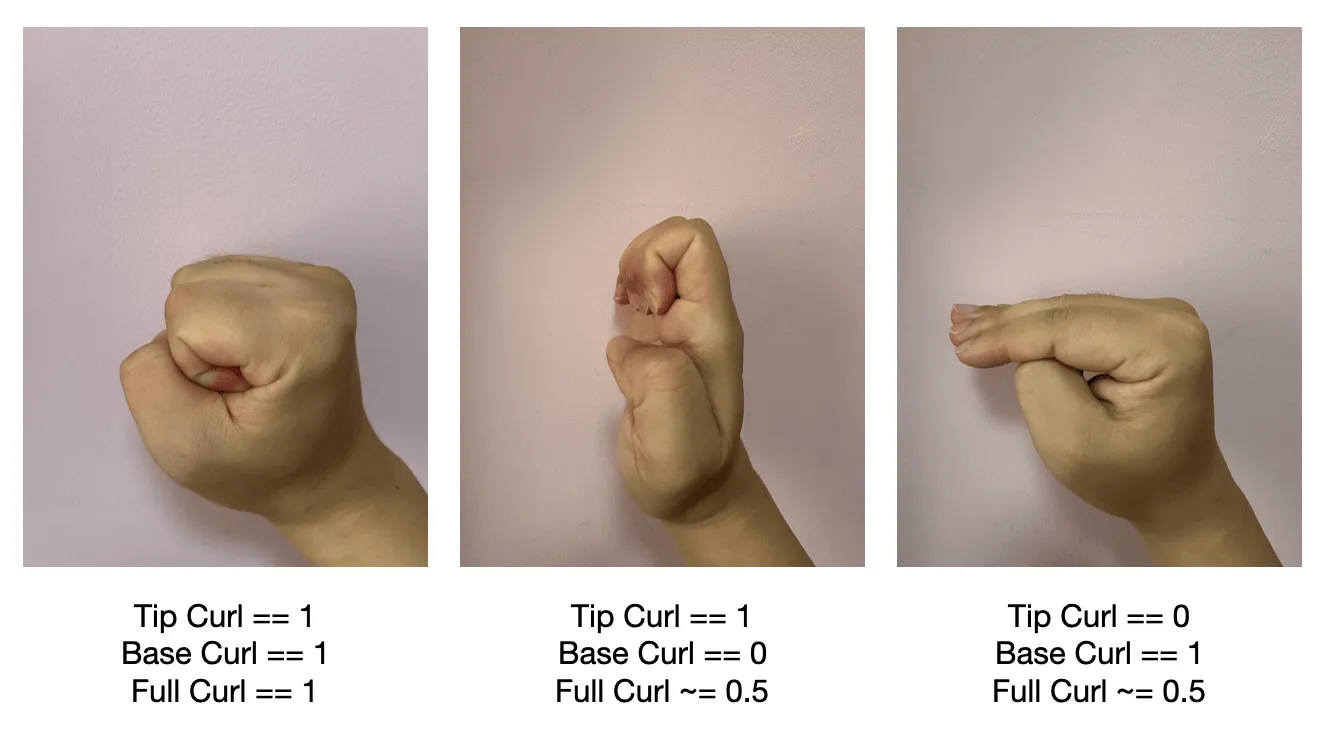
- Finger root curl baseCurl : the curl of the finger root joint, the thumb is the
IntermediateBasejoint, the rest of the fingers are theKnucklejoint, range 0~ 1
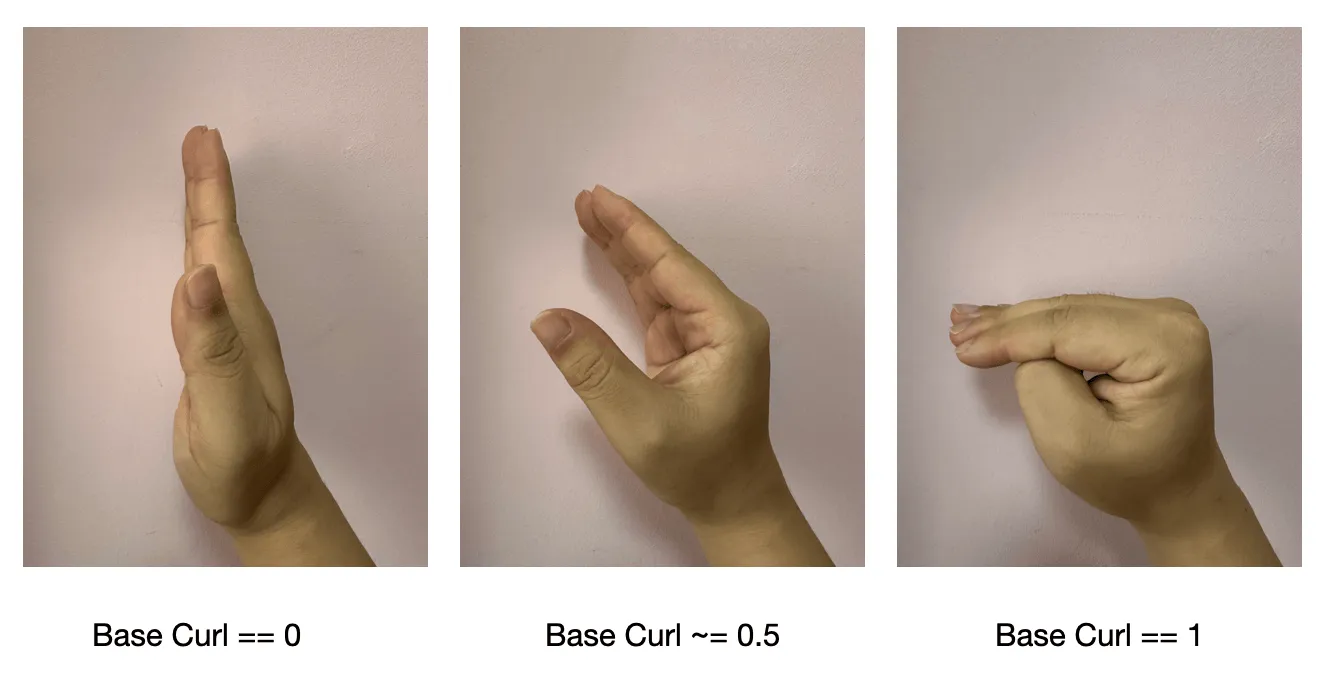
- Fingertip curl tipCurl : the curl of the upper joint of the finger, the thumb is the
IntermediateTipjoint, and the rest of the fingers are the average of theIntermediateBaseandIntermediateTipjoints, ranging from 0 to 1
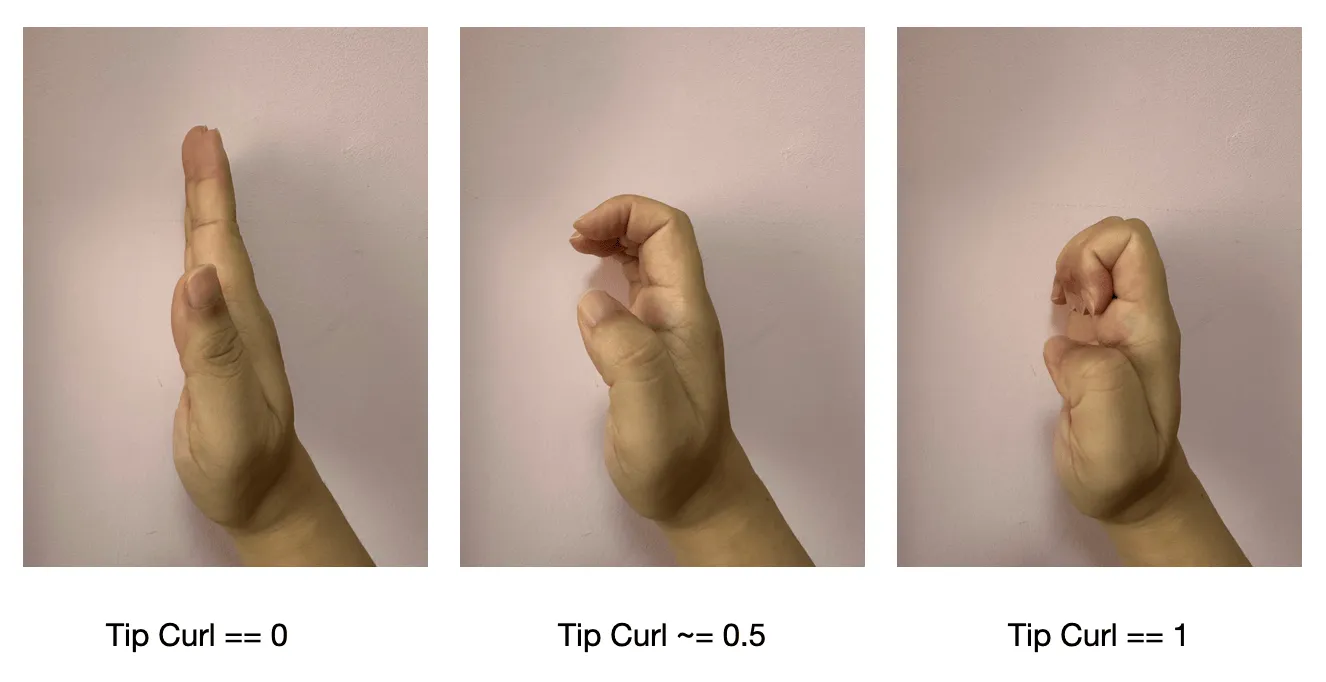
- Overall curl fullCurl : the average value of baseCurl and tipCurl, range 0~ 1
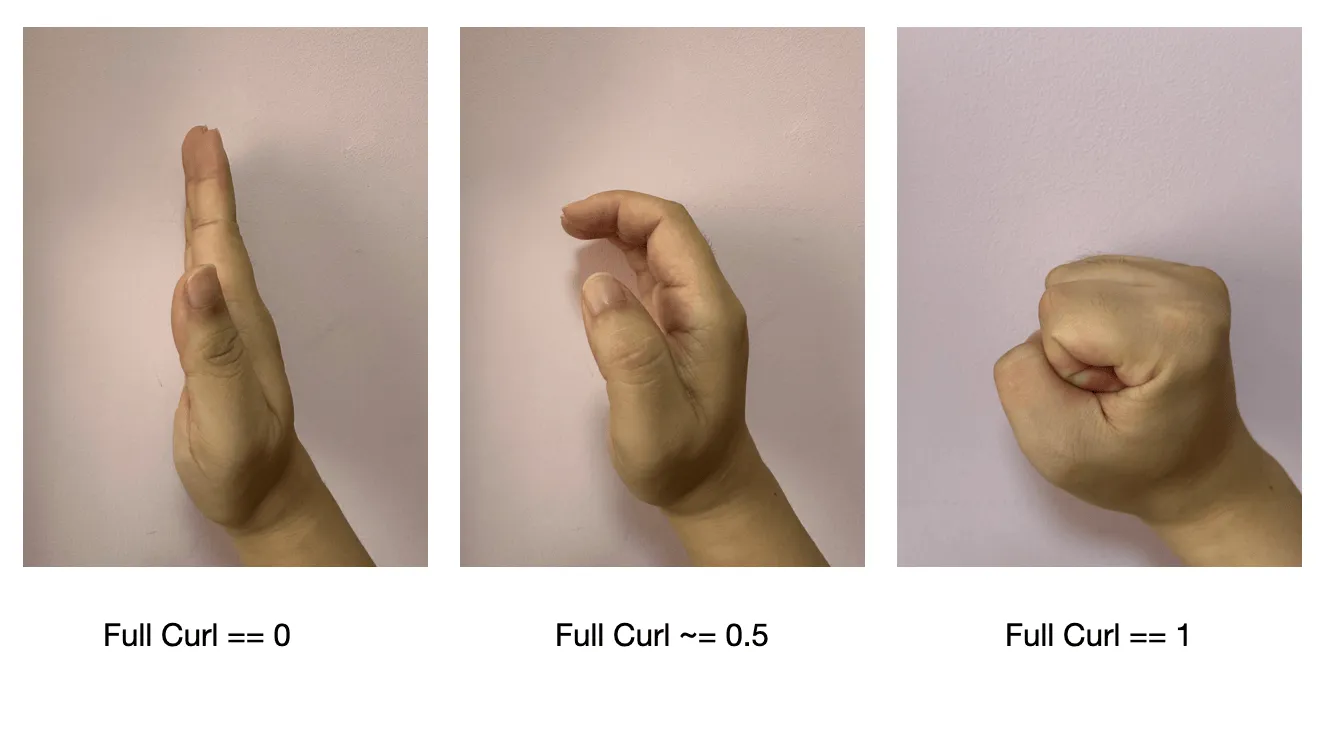
- (With the thumb) pinch : calculate the distance from the tip of the thumb, range 0~ 1, the parameter of the thumb is
nil
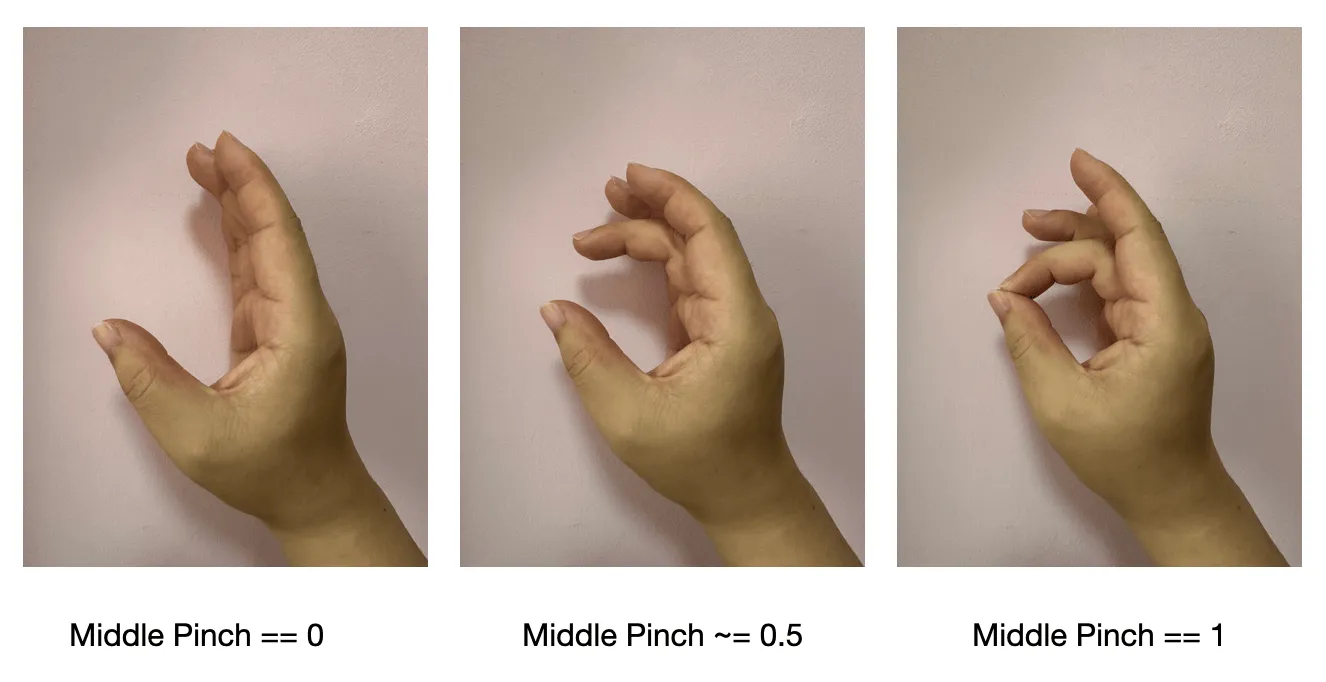
- (Adjacent fingers on the outside) separation spread : only calculate the angle in the horizontal direction, range 0~ 1, the parameter of the little finger is
nil
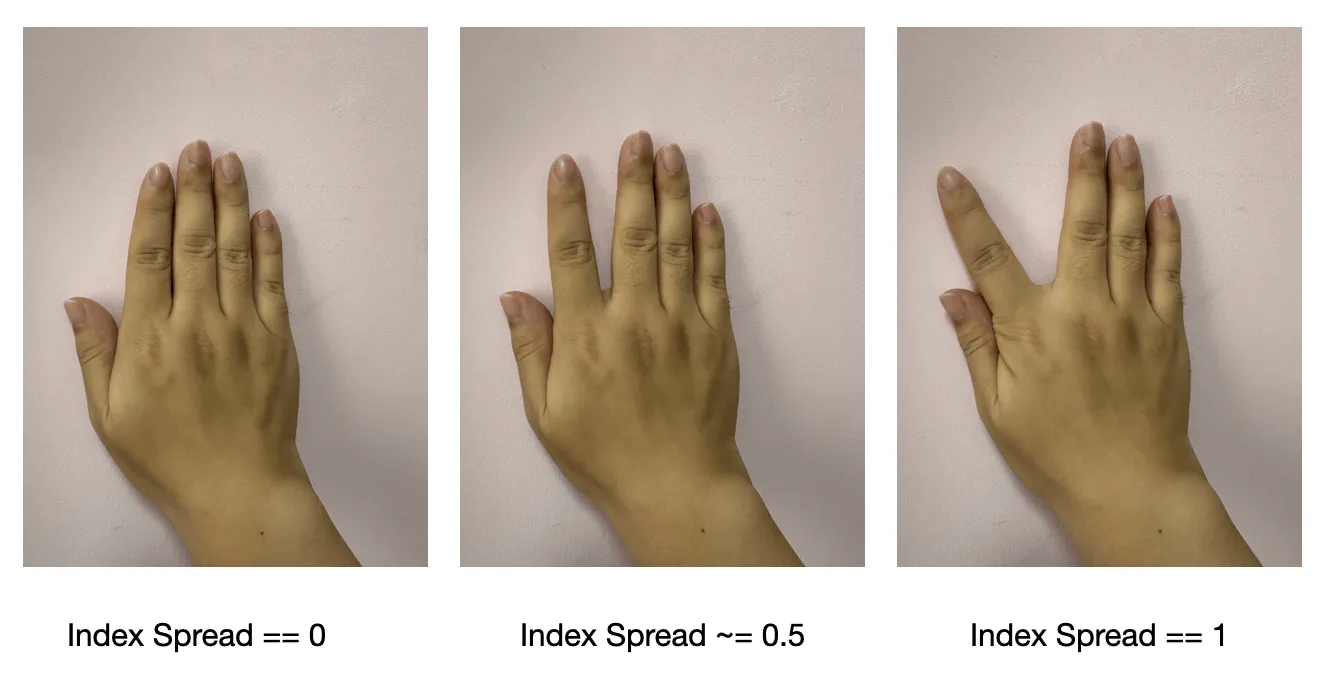
Regarding the differences between the three different curvatures, please refer to the following figure.
SimHand Update
The emulator debugging function has always been a highlight feature of HandVector , but after the 2.0 update changed the vector coordinate system, it brought huge trouble: Google’s MediaPipes implemented 3D gesture tracking, only the position of the joint point, no matrix information!!!
This means I need to use a lot of math “black magic” to create matrix information out of nothing! These complex codes took nearly a week to write and debug, and I was ready to give up several times in the middle…
// 令人头秃的“黑魔法”运算代码
private static func calculateJointTransform(jointDict: [HandSkeleton.JointName: Joint], rootTransform: simd_float4x4, isLeft: Bool) -> [HandSkeleton.JointName: simd_float4x4] {
var worldTransforms: [HandSkeleton.JointName: simd_float4x4] = [:]
// thumb transform need refer palm center
let knukleCenter = (jointDict[.indexFingerKnuckle]!.position + jointDict[.middleFingerKnuckle]!.position + jointDict[.ringFingerKnuckle]!.position + jointDict[.littleFingerKnuckle]!.position) / 5.0
let palmCenter = knukleCenter + jointDict[.wrist]!.position / 5.0
let palmOffset = palmCenter + rootTransform.columns.1.xyz * (isLeft ? 0.035 : -0.035)
// thumbIntermediateBase
let thumbInterBaseX = normalize(jointDict[.thumbIntermediateTip]!.position - jointDict[.thumbIntermediateBase]!.position) * (isLeft ? 1 : -1)
let thumbInterBaseY = normalize(palmOffset - jointDict[.thumbIntermediateBase]!.position) * (isLeft ? 1 : -1)
let thumbInterBaseZ = cross(thumbInterBaseX, thumbInterBaseY)
worldTransforms[.thumbIntermediateBase] = simd_float4x4(SIMD4(thumbInterBaseX, 0), SIMD4(thumbInterBaseY, 0), SIMD4(thumbInterBaseZ, 0), SIMD4(jointDict[.thumbIntermediateBase]!.position, 1))
......
let rootZ = rootTransform.columns.2.xyz
// indexFingerMetacarpal
let indexMetaX = normalize(jointDict[.indexFingerKnuckle]!.position - jointDict[.indexFingerMetacarpal]!.position) * (isLeft ? 1 : -1)
let indexMetaY = cross(rootZ, indexMetaX)
let indexMetaZ = cross(indexMetaX, indexMetaY)
worldTransforms[.indexFingerMetacarpal] = simd_float4x4(SIMD4(indexMetaX, 0), SIMD4(indexMetaY, 0), SIMD4(indexMetaZ, 0), SIMD4(jointDict[.indexFingerMetacarpal]!.position, 1))
......
}
Fortunately, with my excellent knowledge of geometry, I successfully reproduced the matrix from its position using code. Although it is not precise enough, it can barely support debugging. One of the major features of HandVector has been preserved.
Other
In addition to the above three major functions, I have also adjusted the project structure and 3D joint style, making the code structure clearer.
In terms of joint visualization, changing from a small sphere to a small cube makes it easier to display the differences between different orientations: the positive direction of the XYZ axis is RGB, and the negative direction is dark RGB.
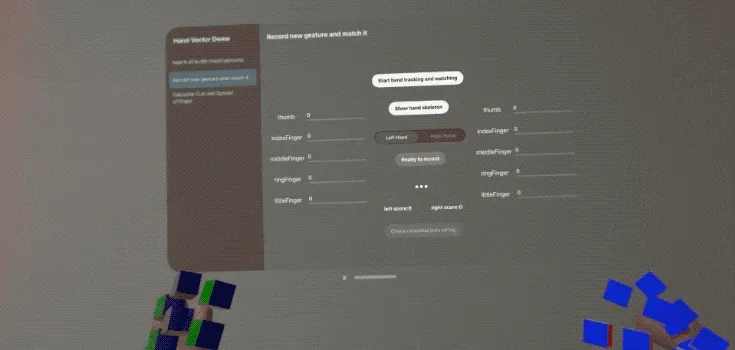
Finally, version 2.0 is still in beta testing, welcome to use and submit feedback.
Reference
Author of this article

Recommended Reading
- Beginner's guide to AR: Exploring Augmented Reality With Apple AR Tools
- What kind of sparks will be created when PICO 4 Ultra meets spatial video? - Mastering spatial video, PICO is also impressive!
- How to Play Spatial Video On iOS 17.2
- Breaking down the details of Meta Quest 3's upgrades to MR technology
- Before developing visionOS, you need to understand the full view of Apple AR technology
- Solving Nested Transparent Objects in RealityKit with Rendering Ordering - Part 2
- If you are a developer of Apple Vision Pro, then you must pay attention to these points
 XReality.Zone
XReality.Zone